14 1: Retained Earnings- Entries and Statements Business LibreTexts
by 24@Help

(iii) Modification of trust terms—(A) State law will not cause trust to fail to satisfy identifiability requirement. A trust will not fail to satisfy the identifiability requirements of this paragraph (f)(5) merely because the trust is subject to State law that permits the trust terms to be modified after the death of the employee (such as through a court reformation or a permitted decanting) and thus, permits changing the beneficiaries of the trust. If a beneficiary of a see-through trust is another trust, the beneficiaries of the second trust will be treated as beneficiaries of the first trust, provided that the requirements of paragraph (f)(2) of this section are satisfied with respect to the second trust. In that case, the beneficiaries of the second trust are treated as having been designated as beneficiaries of the employee under the plan. (iii) Disability defined for individual who is not age 18 or older.
Adjust for Changes in Current Assets and Liabilities
In the case of an employee who is a 5-percent owner, the employee’s required beginning date is April 1 of the calendar year following the calendar year in which the employee attains the applicable age. The applicable age is determined using the employee’s date of birth as set forth in this paragraph (b)(2). (2) Effective date for section 401(a)(9)(H)—(i) General effective date. Except as otherwise provided in this paragraph (b)(2), section 401(a)(9)(H) applies with respect to employees who die on or after January 1, 2020. However, in the case of a governmental plan (as defined in section 414(d)), section 401(a)(9)(H) applies with respect to employees who die on or after January 1, 2022. The regulations would not have federalism implications, impose substantial direct compliance costs on State and local governments, or preempt State law within the meaning of the Executive order.

Prepare the Operating Activities Section of the Statement of
If the employee and the employee’s spouse are married on January 1 of a distribution calendar year, but do not remain married throughout that year (that is, the employee or the employee’s spouse dies or they become divorced during that year), the employee will not fail to have a spouse as the employee’s sole beneficiary for that year merely because they are not married throughout the accumulated net amount of revenue less expenses and dividends is reflected in the balance of that year. However, the change in beneficiary due to the death or divorce of the spouse in a distribution calendar year will be effective for purposes of determining the applicable denominator under section 401(a)(9) and this paragraph (c) for the following calendar years. Employer N maintains a defined contribution plan, Plan Y. Employee F died in 2025 at the age of 60.
- Increase your desired income on your desired schedule by using Taxfyle’s platform to pick up tax filing, consultation, and bookkeeping jobs.
- Nonmonetary assets include assets where measurement is uncertain.
- If the alternate payee dies after distribution of the alternate payee’s separate account has begun (determined under §1.401(a)(9)-2(a)(3)) but before the employee dies, distribution of the remaining portion of that portion of the benefit allocated to the alternate payee must be made in accordance with the rules in §1.401(a)(9)-5(c) or §1.401(a)(9)-6(a) for distributions during the life of the employee.
- Although retained earnings are not themselves an asset, they can be used to purchase assets such as inventory, equipment, or other investments.
- B would like to roll over the distribution to B’s own IRA to the extent the distribution does not constitute a required minimum distribution.
§1.1248-1 Treatment of gain from certain sales or exchanges of stock in certain foreign corporations.

There are two generally accepted methods for preparing the operating activities section of the SCF, namely the direct method and the indirect method. This chapter illustrates the indirect method because it is more commonly used in Canada. Both methods result in the same cash flows from operating activities — it is the way in which the number is calculated that differs. The method used has an impact on only the operating activities section and not on the investing or financing activities sections.
Summary of Investing and Financing Transactions on the Cash Flow Statement

If all or any portion of an eligible rollover distribution that is rolled over to a Roth IRA is not from a designated Roth account described in section 402A, then the amount rolled over to the Roth IRA is included in the employee’s gross income to the extent required under section 402(a). However, the amount rolled over to a Roth IRA generally is not subject to the 10-percent additional income tax under section 72(t). If a distributee of an eligible rollover distribution does not elect to have the eligible rollover distribution paid directly from the plan to an eligible retirement plan in a direct rollover under section 401(a)(31), the eligible rollover distribution is subject to mandatory income tax withholding under section 3405(c). See §31.3405(c)-1 of this chapter for provisions relating to the withholding requirements applicable to eligible rollover distributions.
If an eligible rollover distribution includes some or all of an employee’s basis and less than the entire distribution is being rolled over, then the amount rolled over is treated as consisting first of the portion of the distribution that is not allocable to the employee’s basis. A distribution from a designated Roth account may be rolled over only to another designated Roth account or to a Roth IRA. A contract that is purchased under a Roth IRA is not treated as a contract that is intended to be a QLAC for purposes of applying the dollar limitation rule in paragraph (q)(2)(ii) of this section. If a QLAC is purchased or held under a plan, annuity, account, or traditional IRA, and that contract is later rolled over or converted to a Roth IRA, the contract is not treated as a contract that is intended to be a QLAC after the date of the rollover or conversion. Thus, premiums paid with respect to the contract will not be taken into account under paragraph (q)(2)(ii) of this section after the date of the rollover or conversion. The applicable percentage is the percentage specified in following table for the adjusted employee/beneficiary age difference, determined in the same manner as in paragraph (b)(2)(iii) of this section.
- This amount reflects the company’s ability to generate profits and reinvest in its operations.
- Accordingly, the minimum distribution requirement with respect to the transferor IRA must still be satisfied.
- An example of a voluntary restriction was General Electric’s annual report statement that cash dividends were limited “to support enhanced productive capability and to provide adequate financial resources for internal and external growth opportunities”.
- Propensity Company had an increase in the current operatingliability for salaries payable, in the amount of $400.
Section 401(a)(9)(C)(i) (as amended by section 114 of the SECURE Act and further amended by section 107 of the SECURE 2.0 Act) defines the required beginning date for an employee (other than a 5-percent owner or IRA owner) as April 1 of the calendar year following the later of the calendar year in which the employee attains the applicable age or the calendar year in which the employee retires. Section 401(a)(9)(C)(v)(I) provides that in the case of an individual who attains age 72 after December 31, 2022, and age 73 before January 1, 2033, the applicable age is 73. Section 401(a)(9)(C)(v)(II) provides that in the case of an individual who attains age 74 after December 31, 2032, the applicable age is 75. For a 5-percent owner or an IRA owner, the required beginning date is April 1 of the calendar year following the calendar year in which the individual attains the applicable age, even if the individual has not retired. It’s important for companies to track their accumulated losses and retained earnings in order to understand their current financial standing.
What are Retained Earnings?
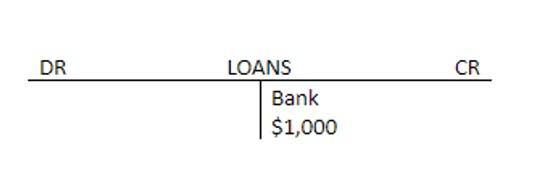
Thus, an addback is necessary to calculate the cash flow from operating activities. Retained earnings is the primary component of a company’s earned capital. It generally consists of the cumulative net income minus any cumulative losses less dividends declared.
F named a testamentary trust (Trust Q), which was established under F’s will, as the beneficiary of all amounts payable from F’s account in Plan X after F’s death. Trust Q satisfies the see-through trust requirements of paragraph (f)(2) of this section. (B) Exercise of power of appointment after September 30 of the calendar year following the calendar year of the employee’s death. (f) Special rules for trusts—(1) Look-through of trust to determine designated beneficiaries—(i) In general. A trust described in the preceding sentence is referred to as a see-through trust. Except as provided in paragraphs (e)(2)(ii) and (iii) of this section and §1.401(a)(9)-8(a) (relating to separate account treatment), if the employee has more than one designated beneficiary, and at least one of those beneficiaries is not an eligible designated beneficiary, then the employee is treated as not having an eligible designated beneficiary.
Explaining Changes in Cash Balance
The following two tables summarize the actuarial methodology used in determining the actuarial present value of the additional benefit. The employee’s remaining life expectancy is determined initially using the employee’s age as of the employee’s birthday in the calendar year of the employee’s death. In subsequent calendar years, the remaining life expectancy is determined by reducing that initial life expectancy by one for each calendar year that has elapsed after that first calendar year. For distribution calendar years up to and including the calendar year that includes the employee’s date of death, the account balance does not include amounts held in a designated Roth account (as described in section 402A(b)(2)).
Recommended Posts
Contra Account: A Complete Guide + Examples Xero accounting
October 8, 2021
Accountants Professional Tax and Accounting Solutions
September 15, 2020